How safe is your hemp? Labs test for contaminants like pesticides, heavy metals, and microbes to ensure products are clean and legal. With hemp’s natural ability to absorb toxins, testing is non-negotiable for safety and compliance.
Key Takeaways:
- Hemp absorbs toxins: Heavy metals (lead, mercury), pesticides, and microbes can contaminate products.
- 93% of hemp products tested in 2024 exceeded the legal THC limit of 0.3%.
- Labs use advanced methods like HPLC for pesticides and ICP-MS for metals.
- HALF BAK’D ensures transparency with QR-accessible Certificates of Analysis (COAs) for every batch.
Why it matters: Without proper testing, consumers risk exposure to harmful substances. HALF BAK’D sets the standard with reliable testing and clear labeling. Scan the QR, trust the product.
21 + only. Hemp-derived; contains < 0.3 % Δ-9 THC (dry weight). Effects may be delayed up to two hours. Check local laws.
Cannabis Laboratory Testing Workflow From Receipt to Results
Common Contaminants Found in Hemp Products
Hemp has a natural ability to absorb substances from its environment, which means it can draw in toxins from the soil and air. This makes thorough lab testing a must for ensuring consumer safety. Let’s dive into some of the most common contaminants, starting with pesticides.
Pesticides and Health Concerns
Pesticides and synthetic fertilizers used during hemp cultivation can stick around in the final products, potentially putting consumers at risk. A 2016 study revealed that 84.6% of cannabis products in Washington state's legal market contained pesticide residues. These chemicals don’t just linger - they become even more concentrated in extracts and oils.
"If pesticides are used in cannabis production, they are concentrated into the final product. The presence of dangerous pesticides have documented health risks... that hinder the process of the neurological, developmental, hormonal, and reproductive systems within the body." – Sarah Russo, Treadwell Farms
To avoid these risks, high-quality hemp is often grown organically. U.S.-grown organic hemp, in particular, is a safer choice, as it significantly reduces the likelihood of pesticide exposure for consumers.
Heavy Metals and Environmental Hazards
Hemp’s ability to pull heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium, and mercury from the soil can be a double-edged sword. While this trait, known as phytoremediation, is great for cleaning up polluted areas, it becomes a serious issue when contaminated plants are used in consumer products. Studies on hemp-based food items have found metals like barium, copper, nickel, and zinc - with zinc levels reaching up to 38 µg/g.
"Hemp is known to accumulate heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, arsenic, mercury, chromium or nickel in its roots, shoots, buds and seeds, and has been used for the remediation of contaminated soil." – Stephan Altmaier, Advanced Analytical R&D, Merck KGaA
Of particular concern are the "big four" heavy metals - arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead - which can cause severe health problems, including organ damage and long-term toxicity. Without proper testing, consumers might unknowingly ingest harmful levels of these substances in products like gummies, vapes, or oils.
Mold, Mycotoxins, and Other Microbial Threats
Beyond chemical contaminants, microbial hazards can also pose significant risks. Bacteria such as salmonella and E. coli can infiltrate hemp products during manufacturing or storage, especially if hygiene standards aren’t up to par. Even more alarming are mycotoxins, toxic compounds produced by molds and fungi. These can develop during growth, processing, or when products are stored in damp conditions. For instance, a water activity level above 0.85 creates an ideal environment for microbial growth.
Residual solvents are another concern. Chemicals like butane or ethanol, often used in the extraction process, can remain in the final product if not thoroughly removed. This makes proper testing and quality control essential to ensure that what ends up on the shelf is both safe and clean.
Lab Testing Methods for Contaminant Detection
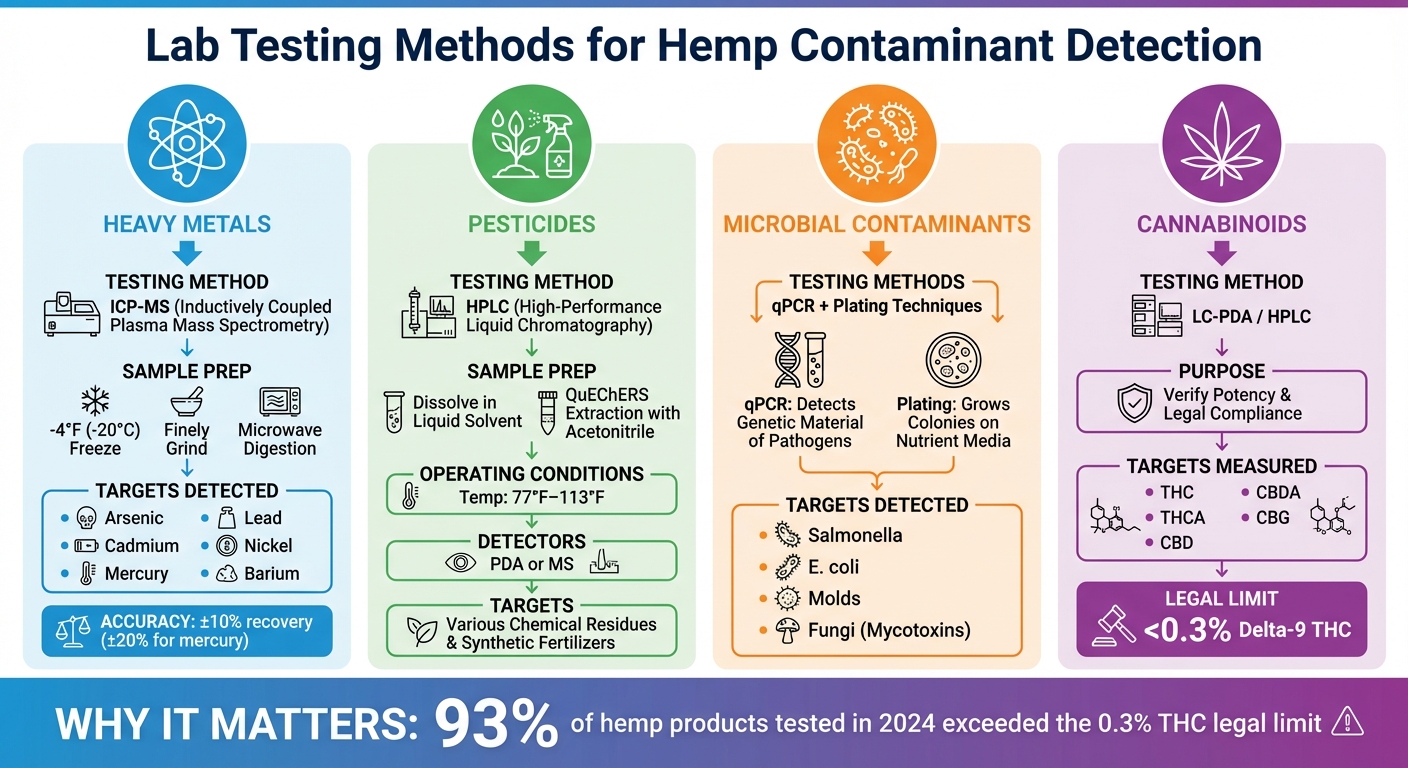
Lab Testing Methods for Hemp Contaminant Detection
When hemp samples arrive at the lab, they undergo rigorous testing using advanced tools designed to identify pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial agents. These precise methods ensure thorough detection and measurement of contaminants.
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) for Pesticides
HPLC is a go-to method for spotting pesticide residues in hemp products. The process starts with dissolving a hemp sample in a liquid solvent and passing it through a stationary phase column. As the sample moves through the column, its chemical components separate based on their interactions with the material inside. Detectors like Photodiode Array (PDA) or Mass Spectrometry (MS) then step in to identify and measure these separated compounds.
One of the standout features of HPLC is its ability to operate at low temperatures (77°F–113°F), which helps preserve sensitive compounds. Walter B. Wilson from NIST highlights its advantages:
"Many forensic laboratories have switched from GCMS to liquid chromatography due to incomplete conversion of THCA to Δ9 THC in the GC inlet resulting in measurement bias."
To further enhance accuracy, labs often pair HPLC with QuEChERS extraction, a method that uses acetonitrile to isolate pesticide residues effectively from complex hemp matrices.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) for Heavy Metals
When it comes to detecting heavy metals, ICP-MS is the gold standard. This highly sensitive technique can pinpoint even trace amounts of toxic metals, including the "big four" - arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead - along with others like chromium, barium, and nickel.
The process begins by freezing the sample at -4°F (≈ -20°C) and grinding it finely to ensure consistency. The sample is then subjected to microwave digestion, which breaks down the plant material, making it easier to measure metal content accurately. For most heavy metals, recovery rates hover around ±10%, though mercury can sometimes show variability up to ±20% .
qPCR and Plating Techniques for Microbial Contaminants
To detect harmful microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi, labs rely on both quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) and traditional plating methods. qPCR homes in on the genetic material of specific pathogens, offering quick detection even at low levels of contamination. Meanwhile, plating involves growing microbial colonies on nutrient-rich media, allowing labs to identify pathogens like Salmonella, E. coli, molds, and fungi that produce mycotoxins.
| Contaminant Category | Primary Testing Method | Common Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | ICP-MS | Arsenic, Cadmium, Mercury, Lead, Nickel, Barium |
| Pesticides | HPLC / LC-MS | Various chemical residues and fertilizers |
| Microbials | qPCR / Plating | Salmonella, E. coli, Molds, Fungi |
| Cannabinoids | LC-PDA / HPLC | THC, THCA, CBD, CBDA, CBG |
sbb-itb-3a0b05a
Sample Preparation and Testing Standards
Homogenization and Sample Integrity
When it comes to hemp testing, ensuring the sample truly represents the entire batch is a top priority. Labs begin by drying the sample until it’s brittle enough to process. If immediate drying isn’t possible, the sample is stored at temperatures of -4°F (-20°C) or lower to maintain its integrity.
Once dried, the entire plant - including flowers, leaves, seeds, twigs, and stems - is ground thoroughly using a centrifugal rotor mill. This step ensures the material is completely uniform, which is critical for consistent cannabinoid and contaminant distribution. After grinding, the sample is divided into two portions: one for immediate analysis and another as a retain specimen for potential future testing.
To ensure accurate results, labs adjust the sample’s moisture content to achieve a consistent weight loss of 5%–12%. This adjustment aligns with dry weight measurement standards. The USDA emphasizes the importance of this process:
"Sample preparation of pre- or post-harvest sample shall require grinding of the sample to ensure homogeneity of plant material prior to testing".
By adhering to these precise homogenization practices, labs can confidently meet strict regulatory requirements.
Regulatory Standards for Lab Testing
Proper sample preparation isn’t just a technical detail - it’s essential for meeting USDA and ISO testing standards. Hemp products must contain less than 0.3% total delta-9 THC to remain compliant with federal law. Exceeding this limit reclassifies the product as a Schedule I controlled substance .
To ensure transparency and accuracy, the USDA mandates that labs calculate and report a Measurement of Uncertainty (MU) alongside every test result. This provides a confidence interval for the reported values. Additionally, while ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accreditation is strongly encouraged to demonstrate technical skill and reliable methods, all labs conducting official THC compliance testing must register with the DEA by December 31, 2024.
Walter B. Wilson of NIST underscores the importance of precise testing methods:
"The ability to determine THCA is important in cannabis samples as it is often present as the primary form of Δ9-THC... method accuracy is of paramount importance since legal actions are based on the resulting measurements".
A 2021 NIST study revealed significant issues with smokable hemp products. Out of 53 samples marketed as legal hemp, 93% exceeded the 0.3% THC threshold. The study also found major discrepancies between product labels and actual lab results, with total THC levels off by as much as 55% and THCA levels by 68%. These alarming differences often trace back to poor homogenization or inadequate sample preparation practices, highlighting the critical role of proper lab protocols.
How HALF BAK'D Ensures Product Quality
Transparency Through Lab Testing
HALF BAK'D takes pride in its commitment to transparency by offering a dedicated Lab Results portal where customers can easily access downloadable Certificates of Analysis (COAs) for all products. Since January 2026, this portal has included third-party test results for specific batches of popular items like Sumo Gummies and Sumo Disposables. These COAs are not just documents - they come with unique Certificate IDs and QR codes that link directly to the testing lab's secure server, ensuring the authenticity of the reports.
Each COA provides a detailed breakdown of testing results, covering critical areas such as:
- Cannabinoid potency: Includes THC-A, THC-P, and Delta-9 THC levels.
- Heavy metals: Screens for harmful elements like arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury.
- Pesticide residues: Tests for up to 100 different chemicals.
- Mycotoxins and residual solvents.
- Microbial contaminants: Checks for harmful bacteria like E. coli and Salmonella.
For vape products, an additional test ensures the absence of Vitamin E Acetate, a thinning agent linked to severe health risks. This thorough testing process directly addresses an alarming issue highlighted by a JAMA study, which revealed that 70% of hemp products misrepresented their potency, with over 20% containing undisclosed THC.
By making these detailed reports easily accessible, HALF BAK'D not only meets but exceeds industry expectations for transparency and consumer trust.
Meeting Consumer Expectations for Quality
HALF BAK'D employs advanced techniques like Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) to ensure the accuracy of THC-A levels in their vapes and Sumo Gummies. HPLC is a standout method because it measures cannabinoids at room temperature, avoiding the heat-induced conversions that could skew results. This precision guarantees that products deliver the advertised potency while adhering to the federal limit of 0.3% Delta-9 THC.
For edibles like the Sumo Sour'd Gummies, HALF BAK'D uses cryogenic grinding to ensure even cannabinoid distribution throughout the product. This meticulous process prevents inconsistencies like those found in a NIST study, which showed that some manufacturers’ THC claims were off by as much as 55%. Additionally, moisture content and water activity are tested to maintain shelf stability and prevent microbial growth over time.
"HPLC... is the preferred instrument for testing cannabis edibles and extracts due to its ability to test samples at room temperature without requiring a catalyst to produce a heat reaction." - ACS Laboratory
HALF BAK'D’s focus on precision and consistency ensures that every product not only meets consumer expectations but also sets a higher standard for quality in the industry.
Conclusion
Lab testing plays a critical role in ensuring hemp products are safe, meet legal standards, and are accurately labeled. These tests screen for harmful chemical residues and microbial threats that could pose risks to consumer health. Since hemp naturally absorbs heavy metals like arsenic, cadmium, mercury, and lead from the soil, precise and thorough testing is non-negotiable.
Staying within legal limits also depends on rigorous lab verification. The federal threshold for delta-9 THC in hemp is set at 0.3%. Yet, a 2024 study revealed that 93% of 53 smokable hemp products tested exceeded this limit, with some showing discrepancies as high as 55%. Without proper testing, consumers could unknowingly purchase products with misleading potency claims.
"Third-party lab results, officially known as Certificates of Analysis (COAs), are vital safeguards in the CBD industry, protecting against mislabeled or counterfeit products." - Neurogan
HALF BAK'D takes this responsibility seriously by implementing top-tier testing protocols. They collaborate with ISO/IEC 17025:2017 accredited and DEA-registered labs to test every batch of their products, from Sumo Gummies to vape cartridges. Each batch comes with transparent, batch-specific Certificates of Analysis, confirming screenings for heavy metals, pesticides, mycotoxins, residual solvents, and microbial contaminants. Opting for thoroughly tested products means choosing safety, legal compliance, and honest labeling with confidence.
21 + only. Hemp-derived; contains < 0.3 % Δ-9 THC (dry weight). Effects may be delayed up to two hours. Check local laws.
FAQs
How do labs test hemp for harmful contaminants?
Labs employ cutting-edge scientific techniques to make sure hemp products are safe and clean, free from harmful substances like pesticides, heavy metals, and mold. For instance, liquid chromatography is commonly used to spot chemical residues, while inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry is a go-to method for detecting and measuring heavy metals. When it comes to identifying microbial contaminants, labs turn to microbiological assays, including culture methods or PCR (polymerase chain reaction), both of which are highly effective.
These thorough testing processes help ensure hemp products are safe and meet strict quality standards, providing consumers with peace of mind about what they’re using.
Why is it crucial to test hemp products for heavy metals?
Hemp plants have a knack for soaking up everything around them, including toxic heavy metals like lead, arsenic, cadmium, and mercury. If no one checks for these contaminants, they can sneak into hemp products, creating serious health risks for anyone who uses them.
That’s why testing is non-negotiable. It guarantees that hemp products are safe to use, meet quality benchmarks, and stay within legal limits. Plus, it helps preserve the plant’s strength and purity, delivering a safer and more enjoyable experience for users.
How can I ensure the hemp products I buy are safe and free from contaminants?
When shopping for hemp products, always check for a Certificate of Analysis (COA) from an independent, accredited lab. This report not only confirms the product’s cannabinoid levels but also ensures it’s been tested for harmful substances like pesticides, heavy metals, mold, and leftover solvents. Trustworthy brands typically make COAs easy to find, linking them to specific batch or lot numbers. You can usually access them on the company’s website or by scanning a QR code on the packaging.
Taking a moment to review the COA ensures the product meets safety and quality standards, giving you peace of mind before you buy.
